The quick answer is: you can use the 2 sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test, and this article will walk you through this process. Comparing Distributions. Often in statistics we need to understand if a given sample comes from a specific distribution, most commonly the Normal (or Gaussian) distribution. For this intent we have the so-called.. The following code shows how to perform a Kolmogorov-Smirnov test on this sample of 100 data values to determine if it came from a normal distribution: #perform Kolmogorov-Smirnov test ks.test(data, "pnorm") One-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test data: data D = 0.97725, p-value < 2.2e-16 alternative hypothesis: two-sided

(PDF) KolmogorovSmirnov Two Sample Test with Continuous Fuzzy Data

Twosample KolmogorovSmirnov test, where D = 0.857, and p = 0.01.... Download Scientific Diagram

SPSS Kolmogorovsmirnov Analysis

Kolmogorov Smirnov Test Tabelle My XXX Hot Girl
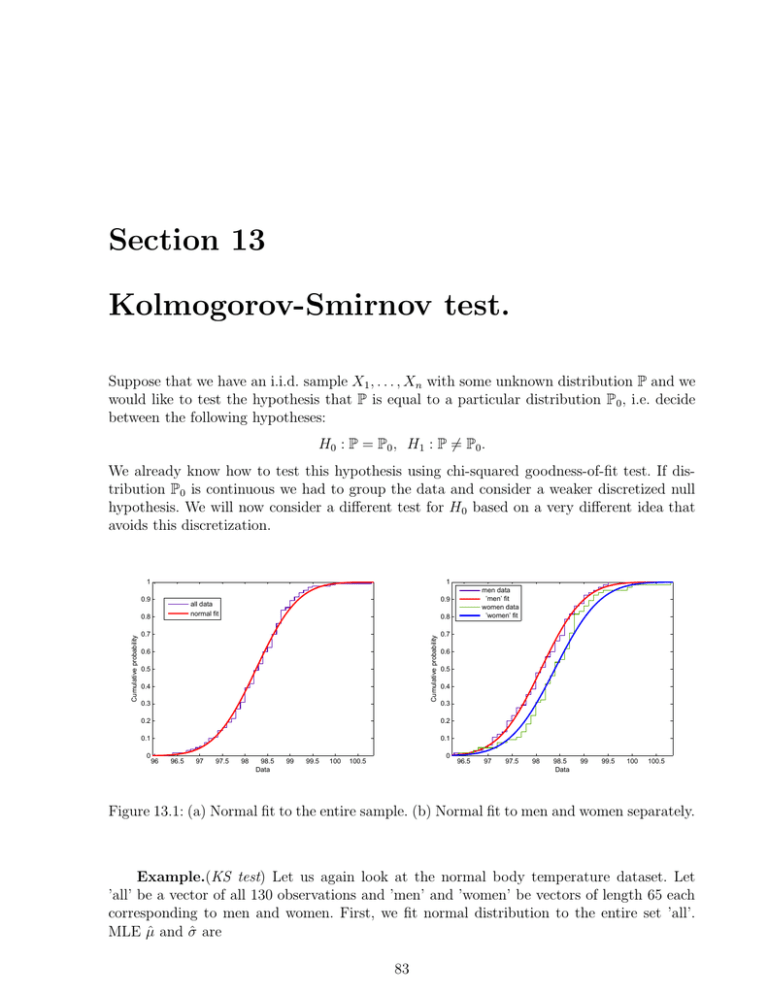
Section 13 KolmogorovSmirnov test.

OneSample KolmogorovSmirnov Test Download Scientific Diagram
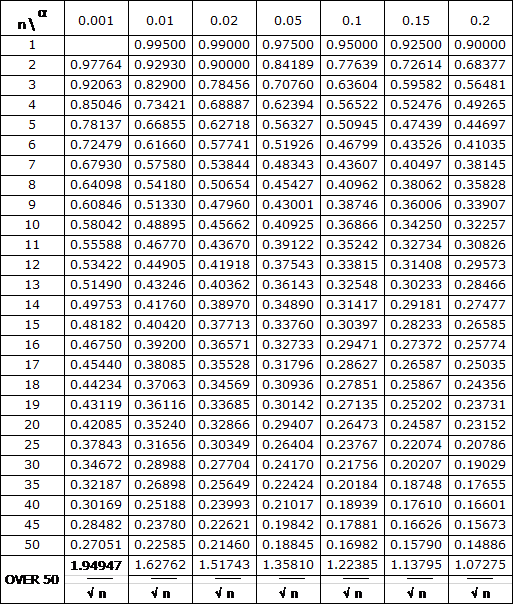
KolmogorovSmirnov Table Real Statistics Using Excel

Twosample Kolmogorov Smirnov test results to determine significant... Download Table

Kolmogorov Smirnov Two Samples Test using SPSS YouTube

hypothesis testing Is 1sample KolmogorovSmirnov test a special case of 2sample one? Cross

Exploring TwoSample KolmogorovSmirnov Test with Simulations

Table 2 from On the KolmogorovSmirnov Test for Normality with Mean and Variance Unknown
[Solved] Twosample KolmogorovSmirnov Test in Python 9to5Answer

Cómo realizar una prueba de KolmogorovSmirnov en Excel Matemáticas aprender nunca había sido

Solved Practice Compute the KolmogorovSmirnov Test

Twosample KolmogorovSmirnov test using standard scores for each... Download Table

OneSample KolmogorovSmirnov Test Download Scientific Diagram

Resources ECE 695A Lecture 33 Model Selection/Goodness of Fit Watch Presentation

Twosample KolmogorovSmirnov test results for Euclidean distance. Download Table

Z KolmogorovSmirnov Test for Two Samples Download Table
Basic Concepts. The two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test is used to test whether two samples come from the same distribution. The procedure is very similar to the One-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test (see also Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test for Normality).. Suppose that the first sample has size m with an observed cumulative distribution function of F(x) and that the second sample has size n with an.. h = kstest2(x1,x2) returns a test decision for the null hypothesis that the data in vectors x1 and x2 are from the same continuous distribution, using the two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.The alternative hypothesis is that x1 and x2 are from different continuous distributions. The result h is 1 if the test rejects the null hypothesis at the 5% significance level, and 0 otherwise.